SSL Certificate
An SSL Certificate is a digital security credential that encrypts
data exchanged between a website and its visitors. It ensures sensitive
information like passwords, payments, and personal details remain
private and protected from cyber threats. SSL also authenticates a
website’s identity, building trust with users. Modern browsers mark
sites without SSL as “Not Secure,” making it essential for credibility,
compliance, and safeguarding online transactions while boosting search
engine rankings.
What is Website SSL Certificate?
SSL stands for Secure Socket Layer. Thus,
SSL
Certificate stands for Secure Socket Layer Certificate which is a protocol
developed to safeguard communication between web browsers and servers.
Its main function is to encrypt data transmitted between two points,
ensuring privacy and security. Over time, SSL has been succeeded by TLS
(Transport Layer Security). But the term "SSL" is still widely used to
refer to website security certificates. An SSL certificate is a digital
certificate installed on a website’s server. It authenticates the
website’s identity and enables an encrypted connection, signified by the
HTTPS prefix in a URL and the padlock symbol in the browser's address
bar. In almost all the web hosting plans, SSL Certificate has to be
bought. However,
Contabo_Web_Hosting gives SSL Certificate for Free with
all its web hosting plans.
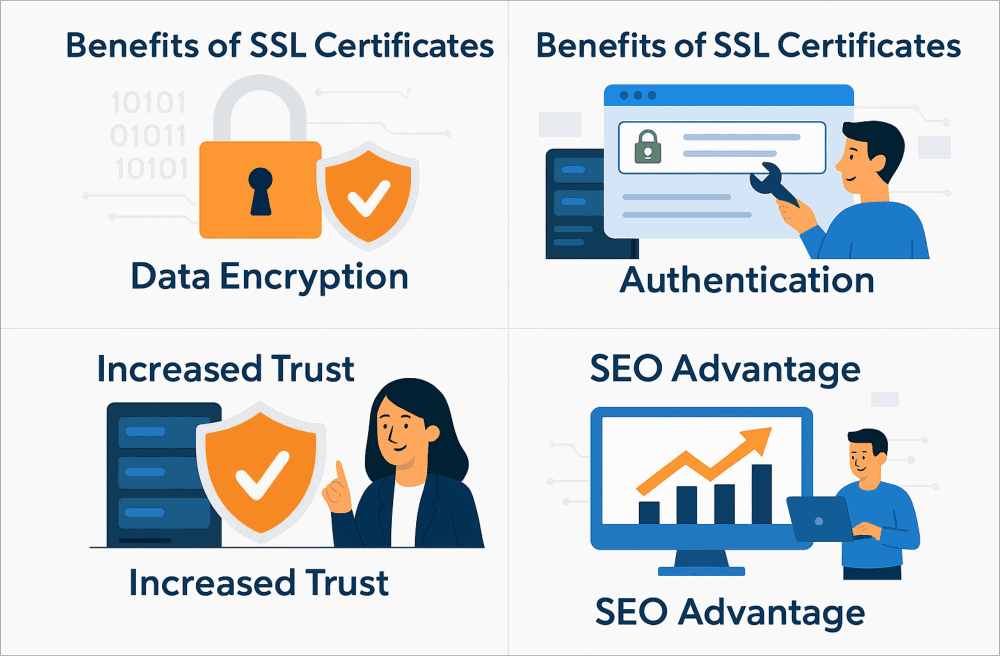
Importance of an SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate ensures secure communication by encrypting data
exchanged between a user and a website, protecting sensitive information
like passwords and financial details. It establishes trust by
authenticating the website's identity, reducing risks of Cyber attacks.
Additionally, search engines prioritize SSL-secured sites, boosting
rankings and credibility. In today’s digital age, it’s an essential tool
for online safety. Having an SSL Certificate is crucial for several reasons:
- Data Security: An SSL
Certificate encryption ensures sensitive information like passwords,
credit card numbers, and personal details remain private.
- Authentication: SSL
certificate validate the website's authenticity, assuring users
they’re interacting with the legitimate site.
- SEO Benefits: Google
prioritizes HTTPS websites in search rankings, making SSL
Certificate vital for visibility.
- Customer Trust:
Displaying HTTPS and the padlock symbol which is only seen when an
SSL Certificate is installed and it instills trust and
confidence in users.
- Compliance: Many
regulations (such as GDPR) require encrypted connections to protect
user data which makes SSL Certificate important.
How Does an SSL Certificate Work?
An SSL Certificate secures online communication by encrypting data
exchanged between a user and a website, ensuring confidentiality. When a
browser accesses a site, the SSL initiates a handshake process,
verifying the site’s authenticity and establishing a secure connection.
SSL Certificates provided by Web Hosting companies like
Contabo_Web_Hosting ensures
Data integrity, Privacy, and Protection against Cyber
threats like eavesdropping or tampering, safeguarding sensitive
information effectively. An SSL certificate operates through a process called the
SSL/TLS handshake, which establishes a secure connection
between the server and browser. Here’s how it works:
- Initiating Connection:
When a user visits a website, the browser requests a secure
connection with the server.
- Authentication: The
server provides its SSL Certificate, which includes a public key and
its identity verified by a Certificate Authority (CA).
- Verification: The
browser checks if the SSL Certificate is valid and is issued by a
trusted CA.
- Encryption: Upon approval of
the SSL Certificate, the browser and server exchange encryption keys
to create a secure channel for data transmission.
- Data Transmission: The
SSL Certificate ensures that all subsequent communication is
encrypted, preventing unauthorized access.
Types of SSL Certificates
Most Web Hosting providers like
Contabo_Web_Hosting
provides Free SSL certificates which come in different types based on validation levels
and functionalities:
-
Domain Validated (DV) Certificates: Domain Validated (DV) certificates provide basic-level security by verifying domain ownership through email or DNS records. They are cost-effective and quick to issue, ideal for personal websites or blogs needing fundamental encryption. DV certificates ensure data is encrypted, but they don't verify organization details, offering less trust compared to higher validation levels like OV or EV certificates.
-
Organization Validated (OV) Certificates: Organization Validated (OV) certificates ensure both domain ownership and the legitimacy of the organization behind the website. Issued after thorough validation, they provide higher trust compared to Domain Validated (DV) certificates. OV certificates display verified organization details, reassuring users of the site's credibility. They are suitable for businesses and institutions requiring enhanced trust and reliable encryption for sensitive data.
-
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: Extended Validation (EV) certificates offer the highest level of security and trust by verifying the legal, physical, and operational existence of the organization. They feature a green address bar or prominent organization name, boosting credibility and user confidence. Ideal for e-commerce and financial websites, EV certificates ensure encrypted data transfer and distinguish legitimate businesses from fraudulent sites effectively.
-
Wildcard SSL Certificates: Wildcard SSL certificates secure a primary domain and an unlimited number of its subdomains under a single certificate. Cost-effective and convenient, they simplify management by avoiding the need for individual certificates for each subdomain. Widely used by businesses with multiple subdomains, Wildcard SSL ensures robust encryption and trust for all components of a domain’s online presence.
-
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates: Multi-Domain SSL certificates, also known as SAN (Subject Alternative Name) certificates, secure multiple domains and subdomains under a single certificate. They simplify management and reduce costs by eliminating the need for separate certificates. Ideal for businesses managing various websites, they ensure encrypted communication and robust security across all included domains, enhancing trust and credibility for online users.
-
Self-Signed Certificates: Self-signed certificates are SSL certificates issued and signed by the website owner, rather than a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). While they provide encryption, they lack authentication and trust, making them unsuitable for public-facing websites. Commonly used for internal testing or development, they can trigger browser warnings, indicating potential risks to users and discouraging secure connections.
Difference Between SSL and TLS
While SSL and TLS are often mentioned together, they’re not
identical. TLS (Transport Layer Security) is the
successor to SSL, offering enhanced security features and performance.
Here’s how they differ:
| Feature | SSL | TLS |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Basic encryption protocols | Advanced encryption algorithms |
| Version | Older, now deprecated | Modern, actively maintained |
| Performance | Slower due to older technology | Faster and more efficient |
| Compatibility | Supported on legacy systems | Widely adopted by modern systems |
Despite the differences, the term "SSL" is still used interchangeably
with "TLS" in most contexts.
Final Words on SSL Certificate
An SSL Certificate or Secure Socket Layer Certificate is a non-negotiable element of modern website
security. It protects user data through encrypted data transmission
between the web hosting server and the client devices, establishes trust, and ensures
compliance with regulatory standards. Understanding SSL working,
types of SSL Certificate, and SSL relationship with TLS can help website owners make
informed decisions and foster secure online interactions. There is
absolutely no difference between paid and free SSL Certificates. You can
get unlimited Free SSL Certificate for all your web hosting needs if you
buy web hosting from this Award Winning
Contabo_Web_Hosting in the mission of Affordable Web
Hosting for Everyone. It costs less than the cost of one coffee a month.
Watch this Video explaining what is SSL Certificate and how important SSL is to a Website.