What is Domain Name
A domain name is the human-friendly address of a website,
like WebHostingShip.com, that replaces complex IP numbers. It
acts as your online identity, guiding users directly to your site.
Domain names are crucial for branding, credibility, and accessibility.
Structured hierarchically with extensions (.com, .org, etc.), they make
websites easy to find, remember, and trust in the digital world.
Domain Name: What is it?
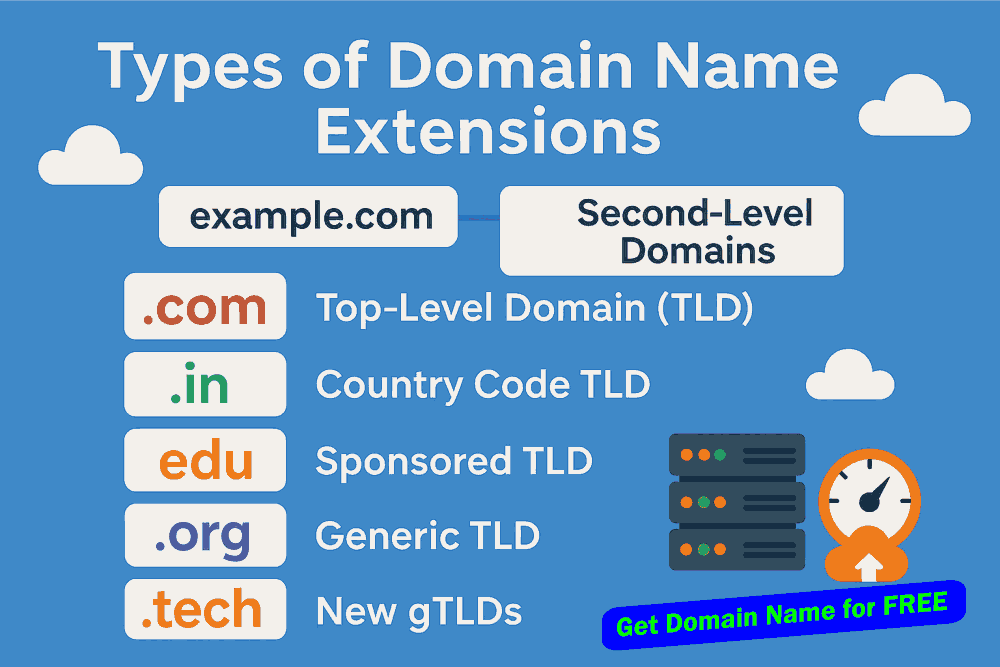
Have you heard of Top-Level Domain (TLD), Country Code TLD, Sponsored
TLD, Generic TLD, New gTLDs, and Second Level Domains? The answer is
simple. Top-Level Domains (TLDs) are the highest level in the domain
name hierarchy, like .com or
.org, Country Code TLDs
(ccTLDs) are Country-specific domain name, such as .in for India, Sponsored TLDs
serve domain names for specific communities like (.edu), Generic TLDs are broad
domain names like (.net),
New gTLDs include fresh domain name options like .tech. Second-Level
Domains sit directly before the TLD, e.g. this website Domain name is,
www.webhostingship.com
A domain name is more than just a web address. It is your gateway to
the digital world. It is the unique identifier name that helps users
locate a specific website on the internet without having to remember
complex numerical IP addresses. In essence, a domain name acts as the
virtual address for a website, much like your home address in the
physical world. Examples include
"bbc.co.uk," and "amazon.in." These names are not just functional; they
are branding tools that signify a company or individual's presence
online. You can buy a Domain name for a few bucks. Most Web Hosting
Companies like
this Award Winning
Contabo_Web_Hosting that
gives a Free Domain Name included along with all their Web Hosting
Plans.
Types of Domain Extensions
A Domain name is classified based on its extension and purpose. Here are the main types of domain name extensions:
-
Top-Level Domains (TLDs): These are the most common and widely recognized domain extensions, such as .com, .org, .net, and .info. They are suitable for general use, with ".com" being the most popular. Examples are google.com, amazon.com, sourceforge.net, wikipedia.org, whoise.info, newegg.biz etc.
-
Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs): These domain extensions represent specific countries or regions, like .in (India), .uk (United Kingdom), and .us (United States). They are often used by businesses or organizations targeting local audiences.
-
Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs): These domain extensions indicate specific industries, organizations, or purposes. Examples include .edu (educational institutions), .gov (government websites), .mil (military), and .biz (businesses). Examples are harvard.edu, mit.edu, nasa.gov, irs.gov, etc.
-
Sponsored Top-Level Domains (sTLDs): These domain extensions are specialized domain names sponsored by certain organizations or communities. Examples include .museum (museums), .aero (aerospace industry), and .jobs (employment-related websites).
-
New gTLDs: Recently introduced domain extensions cater to niche needs and industries like .tech, .store, .online, and .app, offering creative branding opportunities. Examples are viatech.tech, emirates.store, get.online, cash.app, open.ai, etc.
-
Second-Level Domains (SLDs): These domain names are directly below the TLDs. For instance, in example.co.uk, "example" is the second-level domain. SLDs are often combined with country-specific TLDs to create meaningful addresses.
Each type of domain name or domain extension serves unique purposes,
offering versatility and customization options based on your goals. You
need to go to a
Domain Registrar to find the best type of Domain Name for
your needs. You can register a Domain Name absolutely for Free when you
buy Web Hosting Plan from
Contabo_Web_Hosting.
Uses of a Domain Name
Owning a domain name comes with a wealth of benefits. Here are some uses of owning a domain name:
-
Online Identity: A domain name helps establish a unique presence on the internet. Whether for personal branding or business purposes, it creates a distinct identity for your website.
-
Credibility and Professionalism: A custom domain name (e.g., webhostingship.com) conveys professionalism and builds trust with visitors, setting you apart from generic, free domain name options.
-
Simplified Access: Domain names make it easy for people to find your website, avoiding the need to remember complex numerical IP addresses.
-
Branding: Your domain name plays a critical role in your branding strategy, reflecting your business name or niche. A memorable domain name can enhance recognition and retention among your audience.
-
Email Hosting: You can use your domain name to create professional email addresses (e.g., contact@yourbusiness.com), adding credibility to your communications.
-
Global Reach: With the right domain name extension, you can target specific audiences whether locally (with a ccTLD like .in for India, .au for Australia, de for Germany, .fi for Finland etc) or globally (with a TLD like .com).
-
Ownership and Control: Owning a domain name gives you full control over your online presence. You can manage its content, redirect visitors to different platforms, or even monetize it.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): A relevant domain name can improve your website’s discoverability on search engines, attracting more visitors.
-
Marketing and Advertising: Domain names can be used in marketing campaigns and advertisements, making it easier for potential customers to remember and visit your site.
-
Resale Value: Premium domain names can become valuable assets over time and can be resold for profit, especially if they are highly sought after.
Owning a domain name is like owning a piece of digital real estate which is essential for anyone looking to make a lasting impression online. Whether you're building a personal blog, a business website, or an online store, a domain name is a powerful tool to elevate your presence in the virtual world. Do you have a particular use in mind for your domain? I'd be glad to explore it further!
How to Get a Domain Name
Acquiring a domain name is a straightforward process. First, decide on a name that reflects your website’s purpose or brand. Then, check its availability on a platform like Contabo_Web_Hosting which is a Domain Registrar that offer a Free Domain Name when you get a Web Hosting Plan from this Award Winning Web Hosting. Most domain registrars allow you to search for various domain extensions (.com, .org, .net, etc.) to find the best match. Once you find an available name, you can register it by paying a small annual fee. Registration is typically affordable, but premium names with high demand might be more expensive. After registration, you’ll also need to connect the domain to a web hosting service to make your website accessible online.